Acne is a common skin condition that affects both males and females, although there may be differences in its prevalence and severity between the genders.
According to a review published in the Journal of Clinical & Aesthetic Dermatology, acne is more prevalent and severe in males during adolescence, but after adolescence, the condition tends to be more common and severe in females. In general, females are more likely to seek treatment for acne than males, which may skew statistics on prevalence.
Some specific statistics on acne in males and females include:
- Prevalence: Acne affects up to 85% of adolescents, with a slightly higher prevalence in males during adolescence. In adults, the prevalence of acne is estimated to be around 12% in females and 3% in males.
- Severity: Females are more likely to experience moderate to severe acne, while males are more likely to have mild to moderate acne.
- Location: Males are more likely to experience acne on the chest and back, while females are more likely to have acne on the lower face and jawline.
If you are concerned about your acne or have questions about treatment options, it's best to consult with a healthcare professional. In this post, let’s understand acne marks and acne scars difference as well as how to avoid acne occurrence.
Acne marks vs. acne scars
Everyone has experienced acne marks one time in their life. Acne marks and acne scars are related to the same skin condition but they have different characteristics.
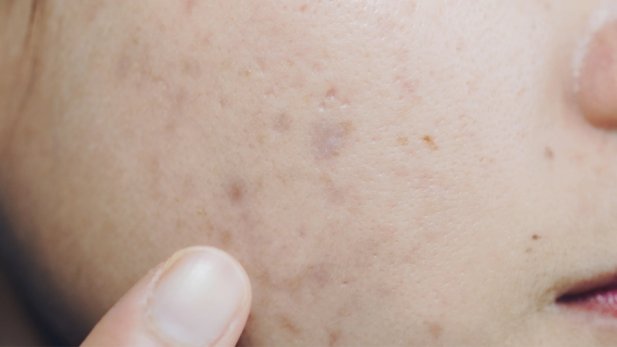
Acne marks, also known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, are flat, discolored areas on the skin that remain after an acne lesion have healed. They are usually red, purple, or brown and are caused by inflammation and increased melanin production during the healing process. Acne marks are not true scars and can fade over time, although it may take several months or longer.
Acne scars, on the other hand, are permanent changes to the skin that occur as a result of severe or prolonged acne. They are caused by the body's natural healing process, which can lead to the formation of scar tissue. Acne scars can take many forms, such as pitted or depressed areas of the skin (known as atrophic scars) or raised, thickened areas (known as hypertrophic scars). They are often more difficult to treat than acne marks and may require professional treatment to improve their appearance.
In summary, acne marks and acne scars are not the same, with marks being temporary and discoloration-based, while scars are permanent and structural changes to the skin.
Oily skin – Acne marks – Acne scars – Are all interrelated?
Yes, there is a relationship between acne marks and oily skin. Acne marks, also known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), can be caused by various factors, including inflammation and trauma to the skin due to acne breakouts. When a pimple forms, it can cause inflammation and irritation to the skin, which can lead to PIH.
Oily skin can contribute to the development of acne by clogging pores with excess oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. When the pores are clogged, it can cause acne breakouts and inflammation, which can lead to PIH.
In addition, oily skin can make it more difficult for acne marks to fade over time. When the skin is oily, it can cause a buildup of sebum and dead skin cells on the surface of the skin, which can prevent new skin cells from forming and hinder the healing process.
Therefore, managing oily skin and treating acne breakouts can help prevent the development of acne marks and promote the healing of existing marks.
How to prevent acne marks occurrence?
Acne marks or scars can be a common concern for people who suffer from acne breakouts. Here are some tips to prevent acne marks from occurring in the first place:
1. Keep your skin clean: Cleanse your skin regularly, especially if you have oily skin. Use a gentle cleanser that doesn't dry out your skin, and avoid scrubbing too hard or using abrasive products.
2. Avoid picking or popping pimples: Picking or popping pimples can increase inflammation and cause scarring. Instead, let the pimples heal on their own.
3. Use non-comedogenic products: Non-comedogenic products are formulated to not clog pores. Choose skincare and makeup products that are labeled as non-comedogenic.
4. Protect your skin from the sun: Sun exposure can worsen acne and lead to dark spots or hyperpigmentation. Wear sunscreen with at least SPF 30 every day, and avoid spending too much time in the sun.
5. Consult a dermatologist: If you have severe acne or are prone to scarring, it's important to seek advice from a dermatologist. They can recommend appropriate treatments to prevent scarring and improve your skin's overall health.
By following these tips, you can help prevent the occurrence of acne marks and maintain healthy, clear skin.